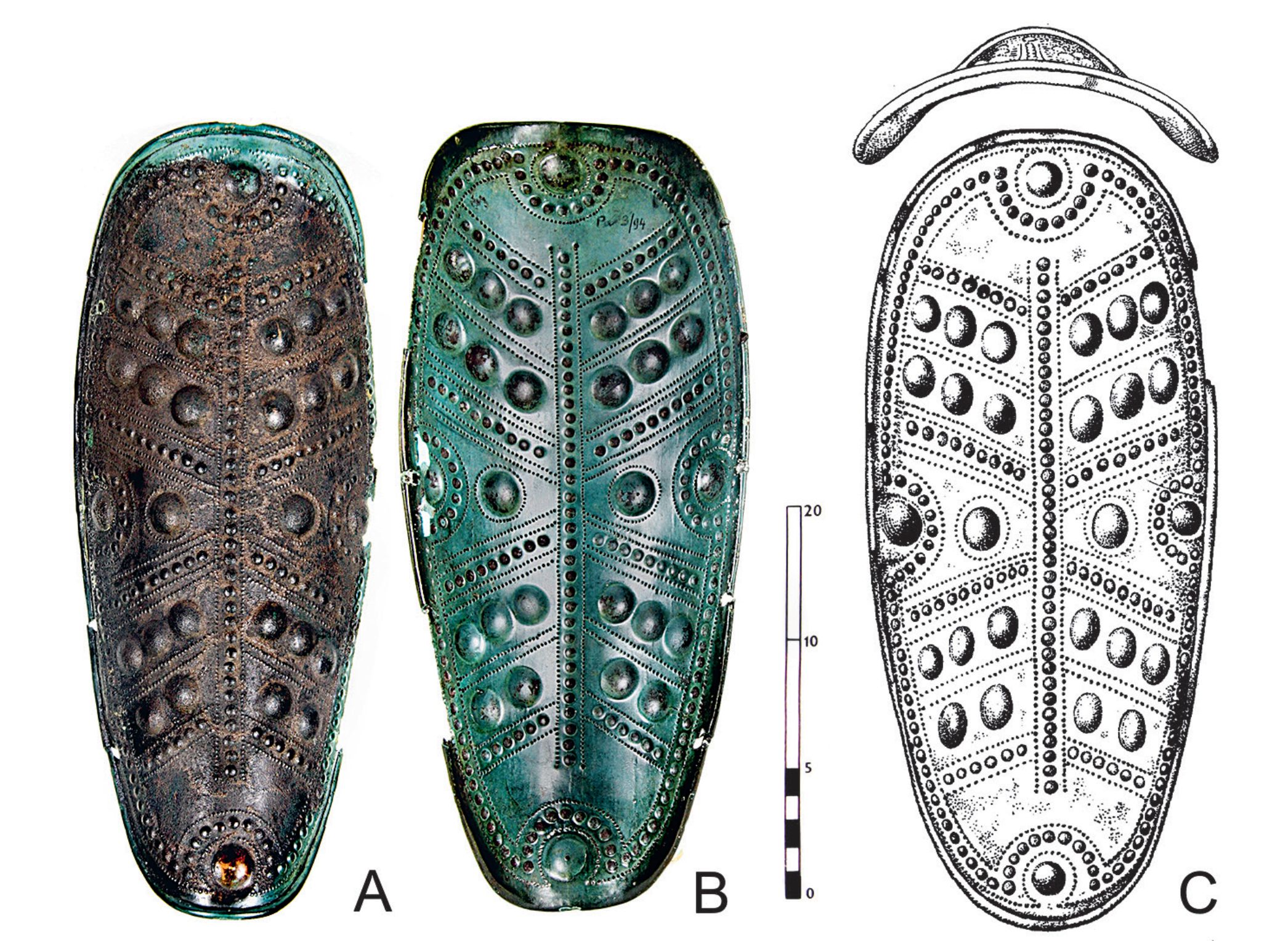
Urnfield period bronze protective armour in Moravia and a contribution to the understanding of bronze cuirasses technology
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.35686/AR.2019.2Keywords:
Moravia, Bronze Age, hoard, protective armour, cuirasses, elemental composition, metallography, leadAbstract
Solid bronze armour components are a phenomenon that first appears in Central European find assemblages at the beginning of the Urnfield culture period. In addition to two parts of bronze helmets (Služín, Brno-Řečkovice) and an old find of a greave (Kuřim), this armour is also documented today in Moravia by a fragment of cuirass (Ivančice 4). The find context is unknown only in the case of the greave; the other artefacts come from hoards and are of Carpathian provenance. Typologically and based on the context of the hoards, the Moravian finds of bronze armour are dated to the period between stages B D2 and Ha B1. According to a material analysis, the sheet metal of the cuirass from the Ivančice 4 hoard is made from classic bronze that was mechanically shaped and subsequently treated by recrystallisation annealing. A bar from a PbSn alloy hammered into the edge of the shoulder cut-out of the cuirass served as a soft ase for bending the edge. Although lead was occasionally made and used already in the period of the Urnfield culture, the find from the Ivančice 4 hoard marked the first time its technological application was demonstrated in the production of bronze cuirasses.
Downloads